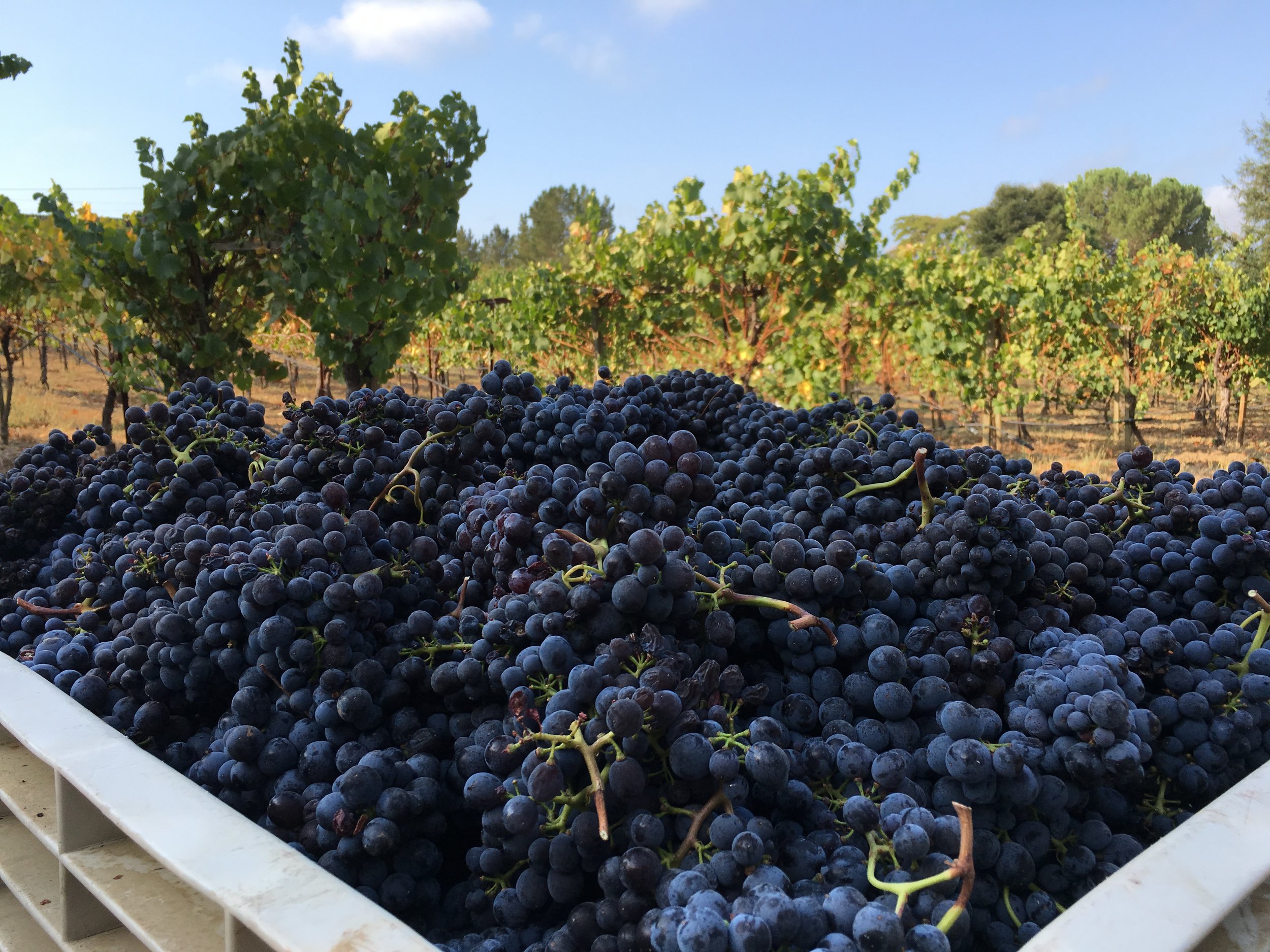
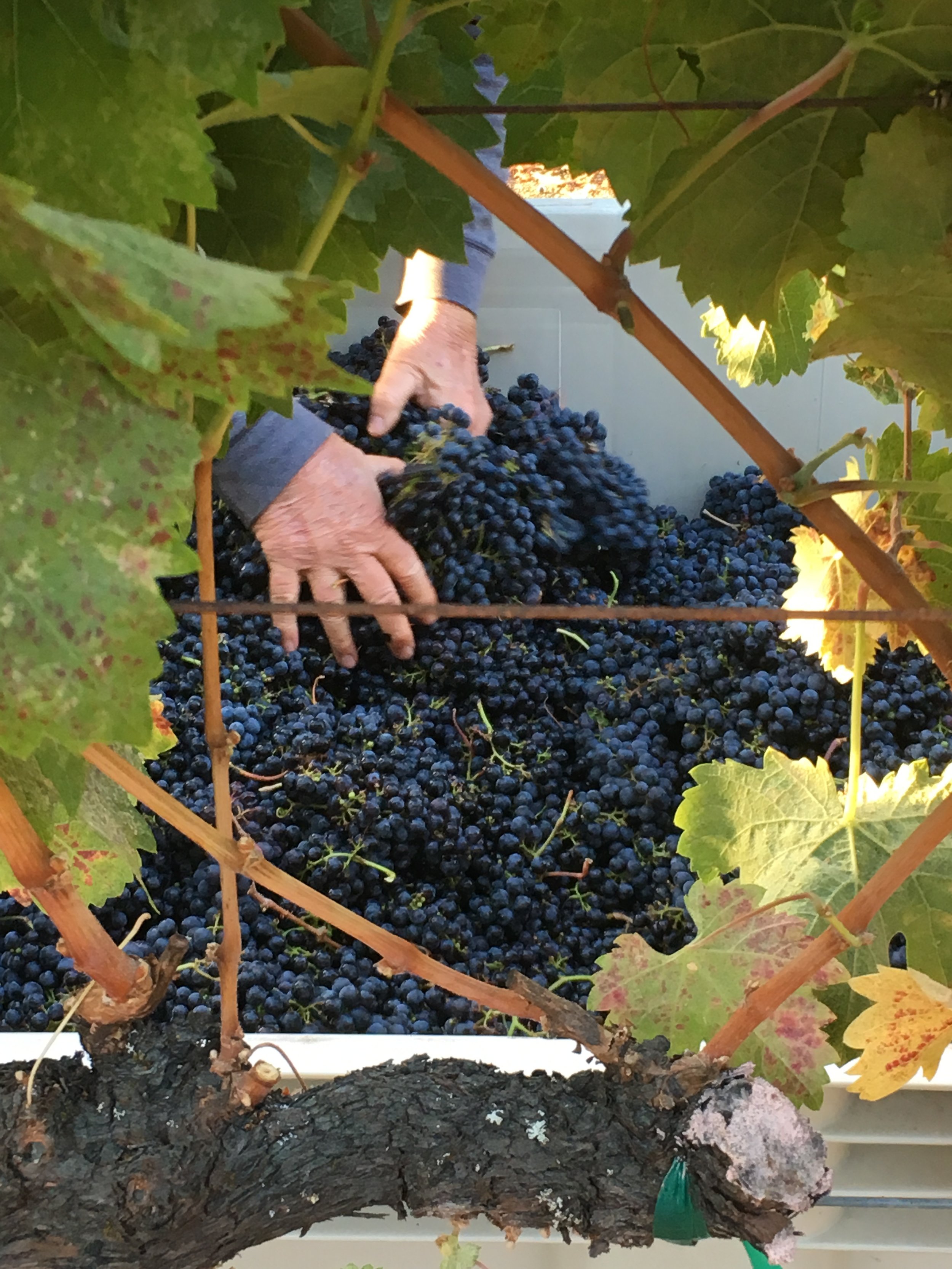
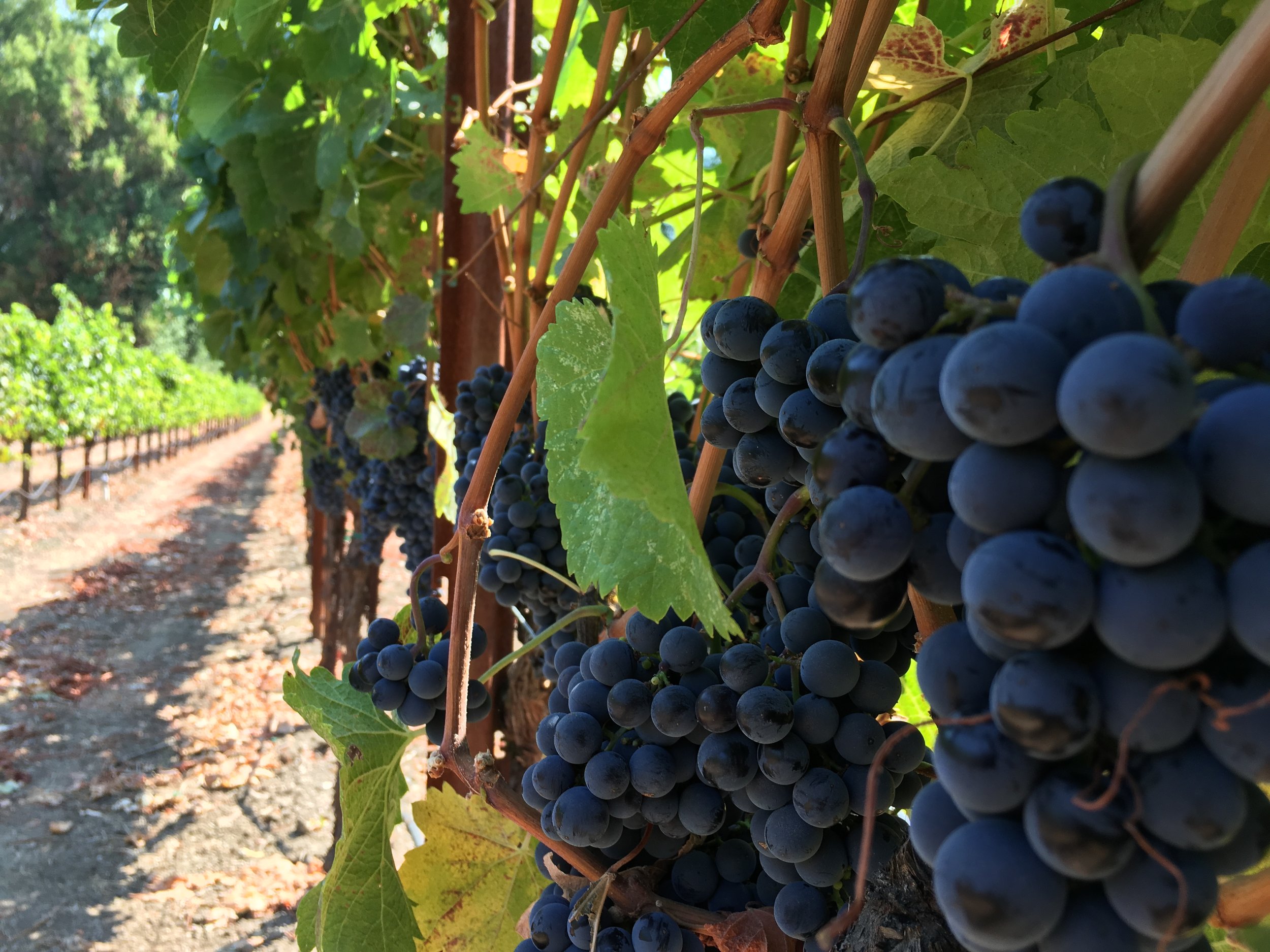
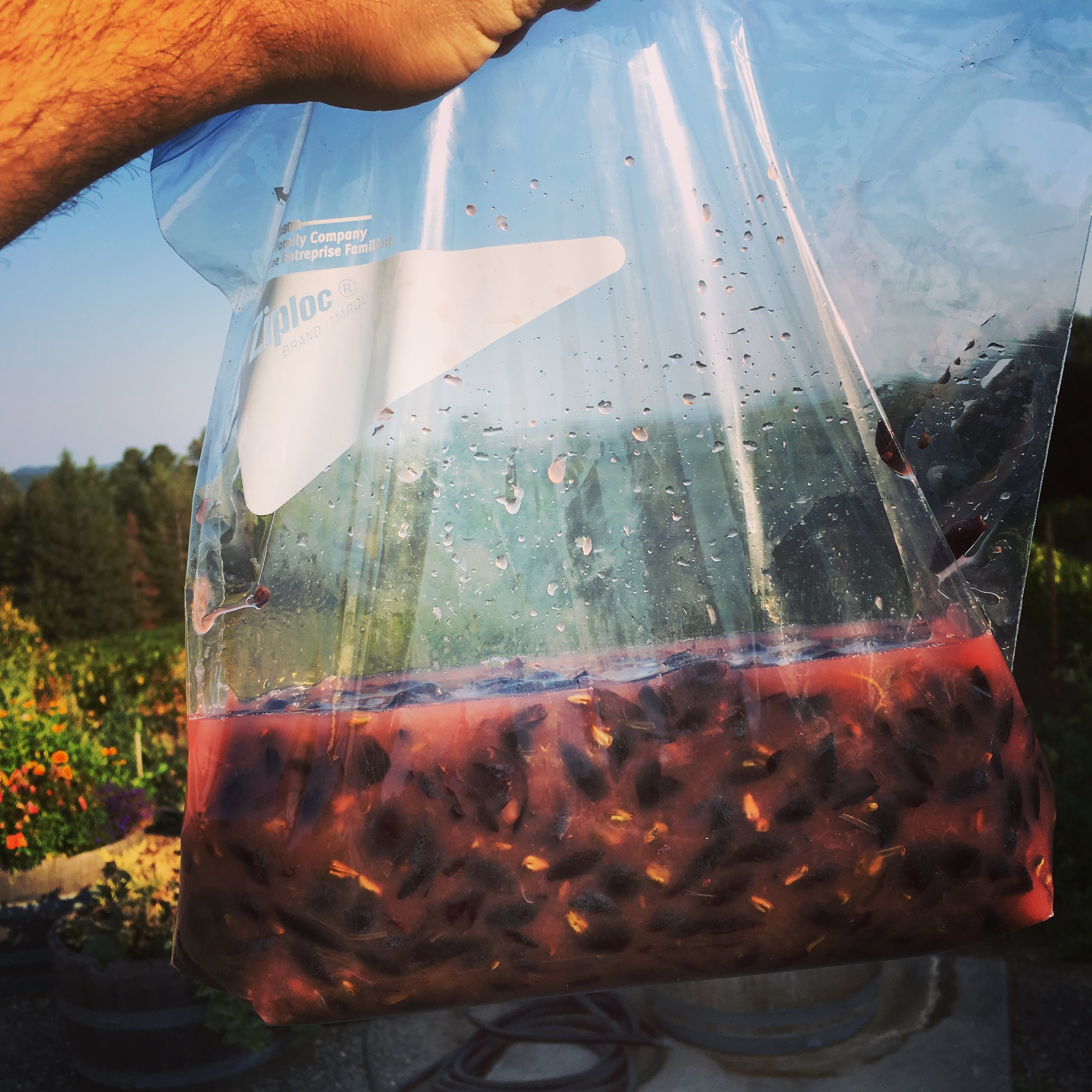
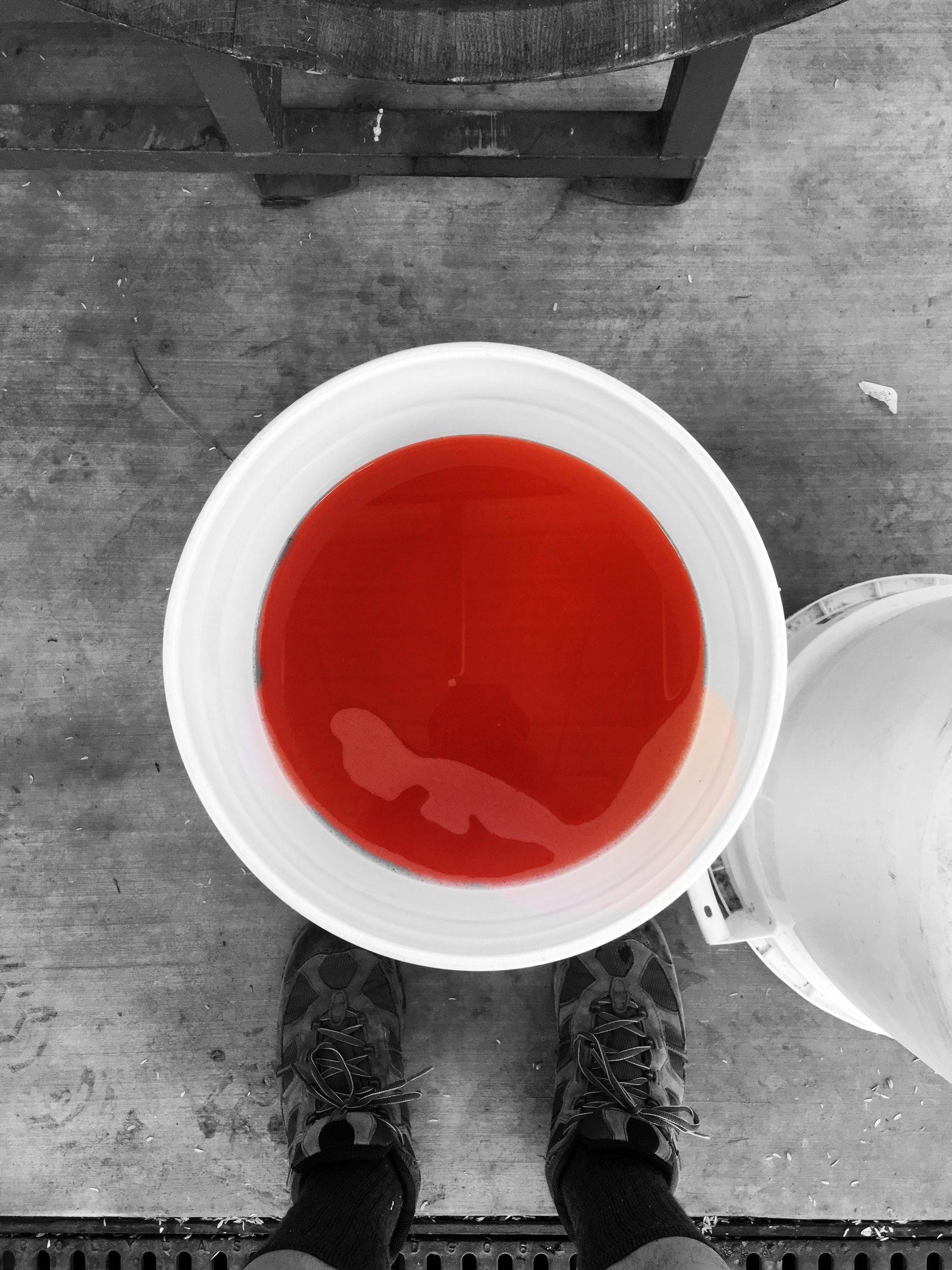
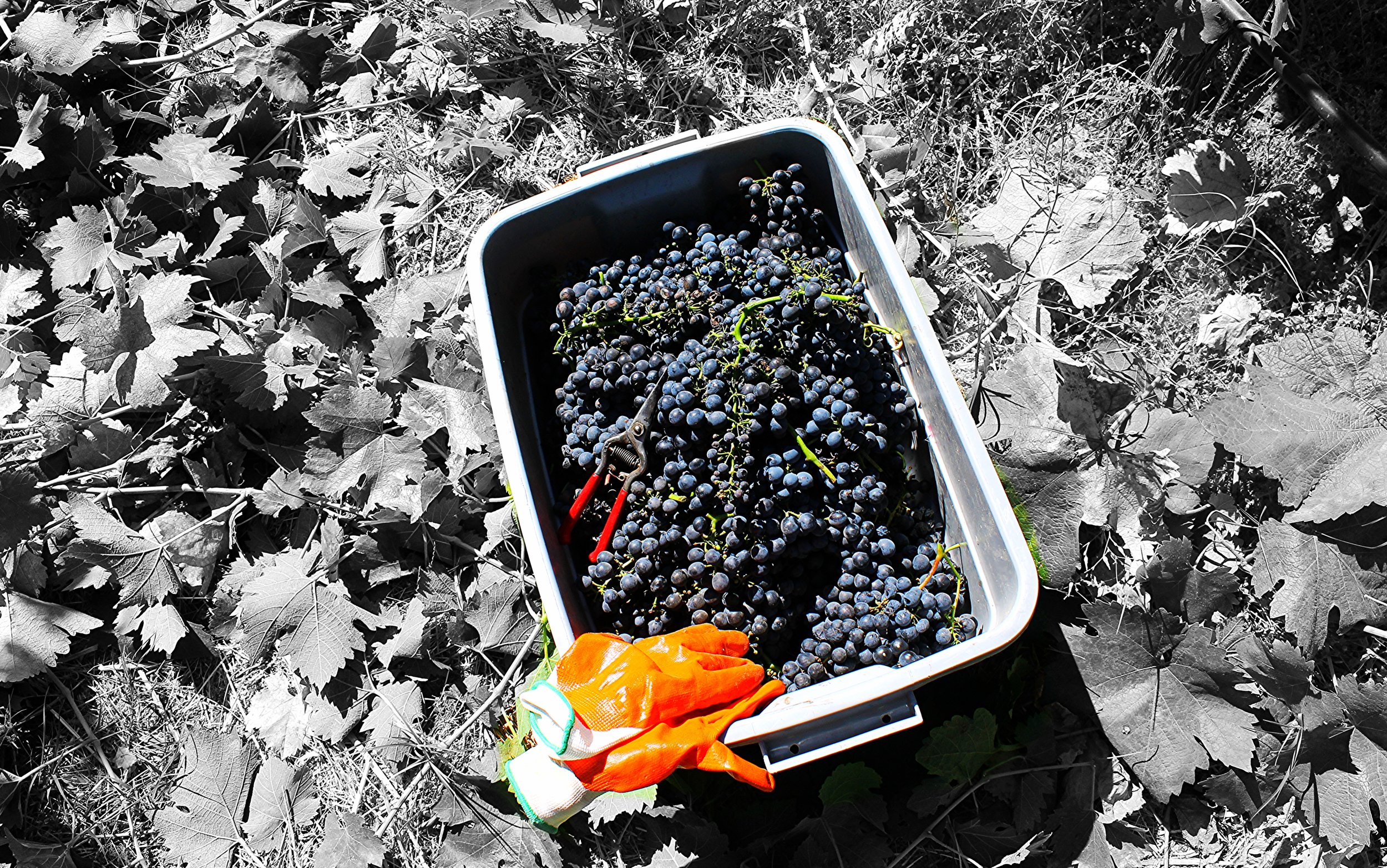
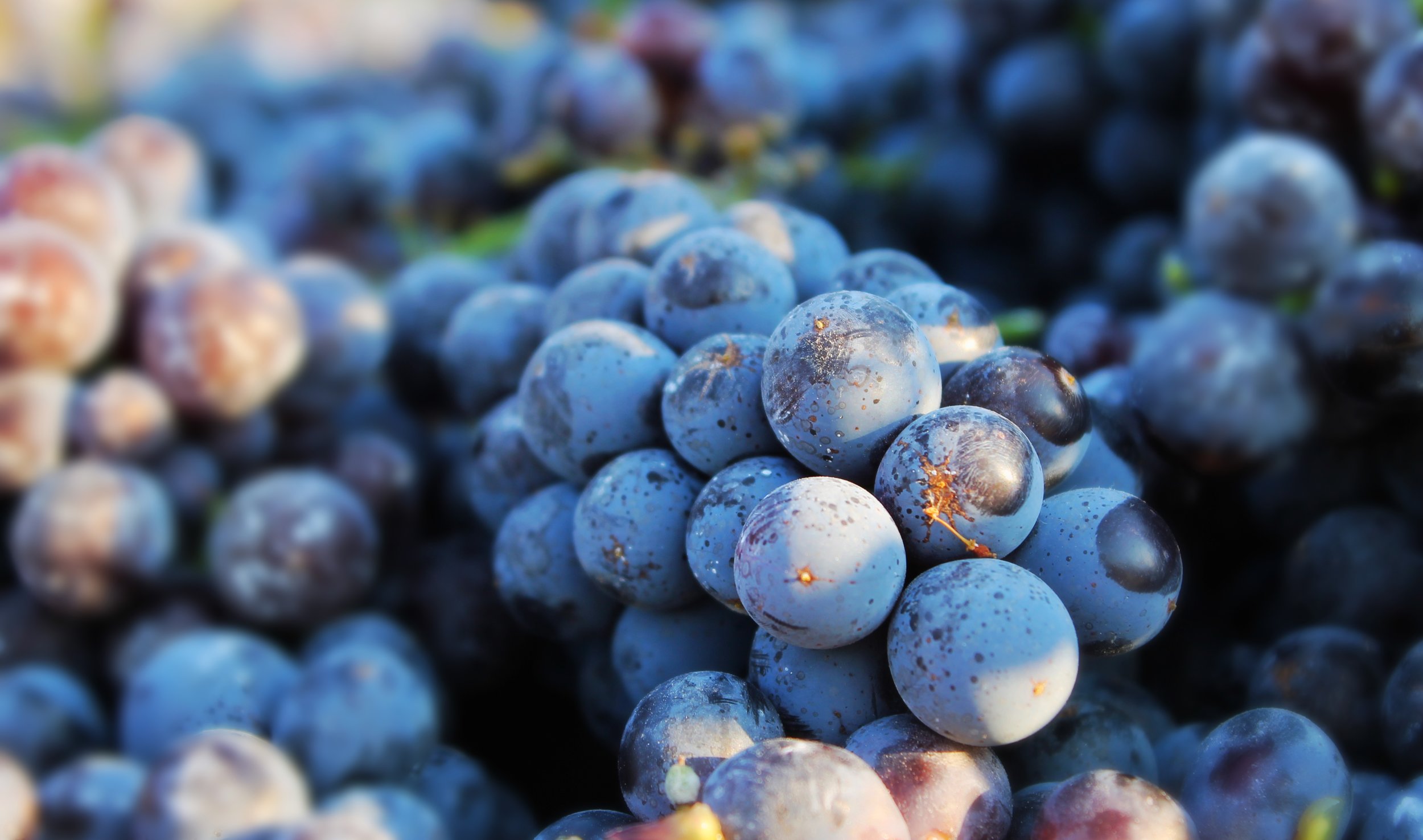
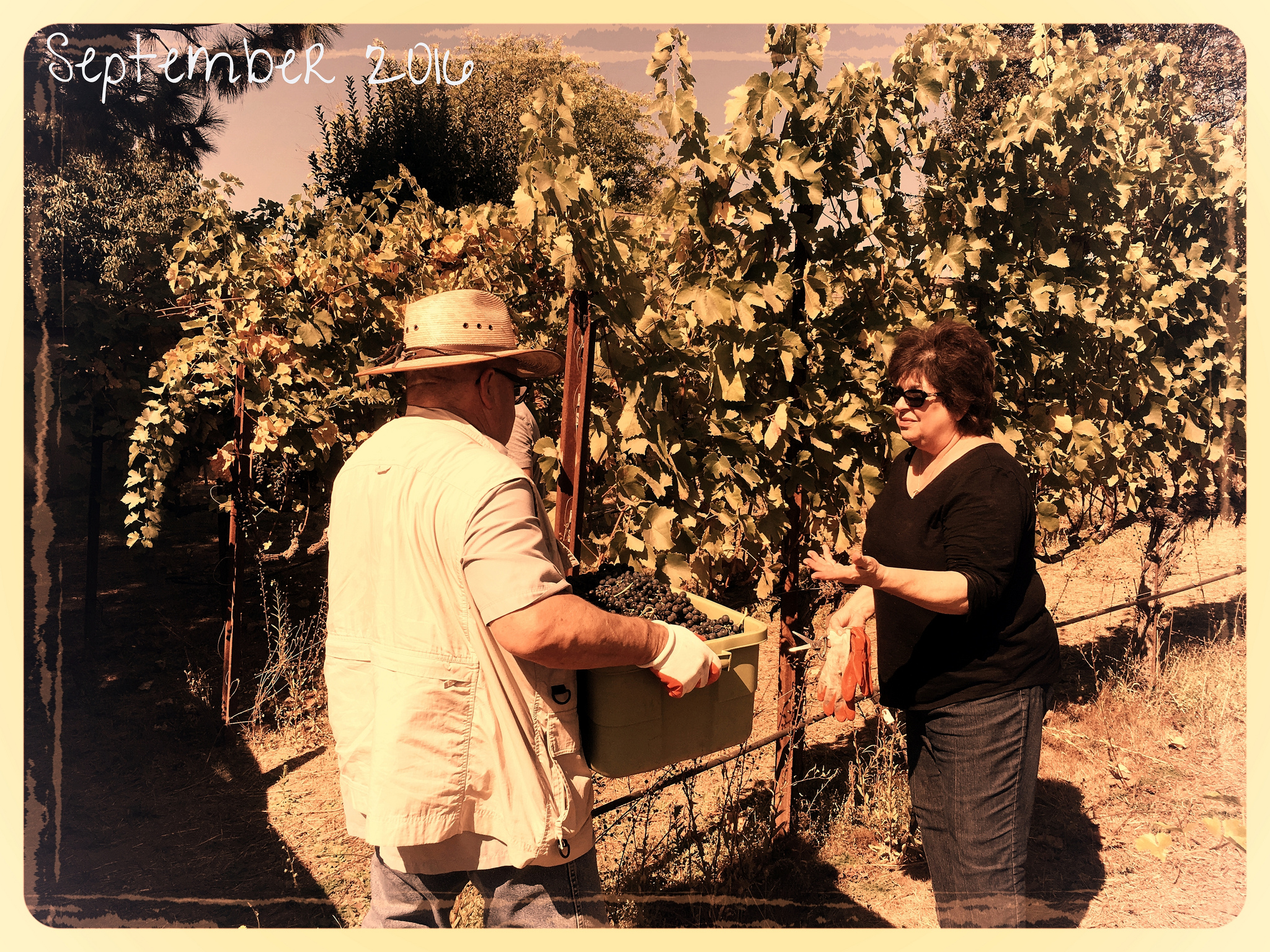
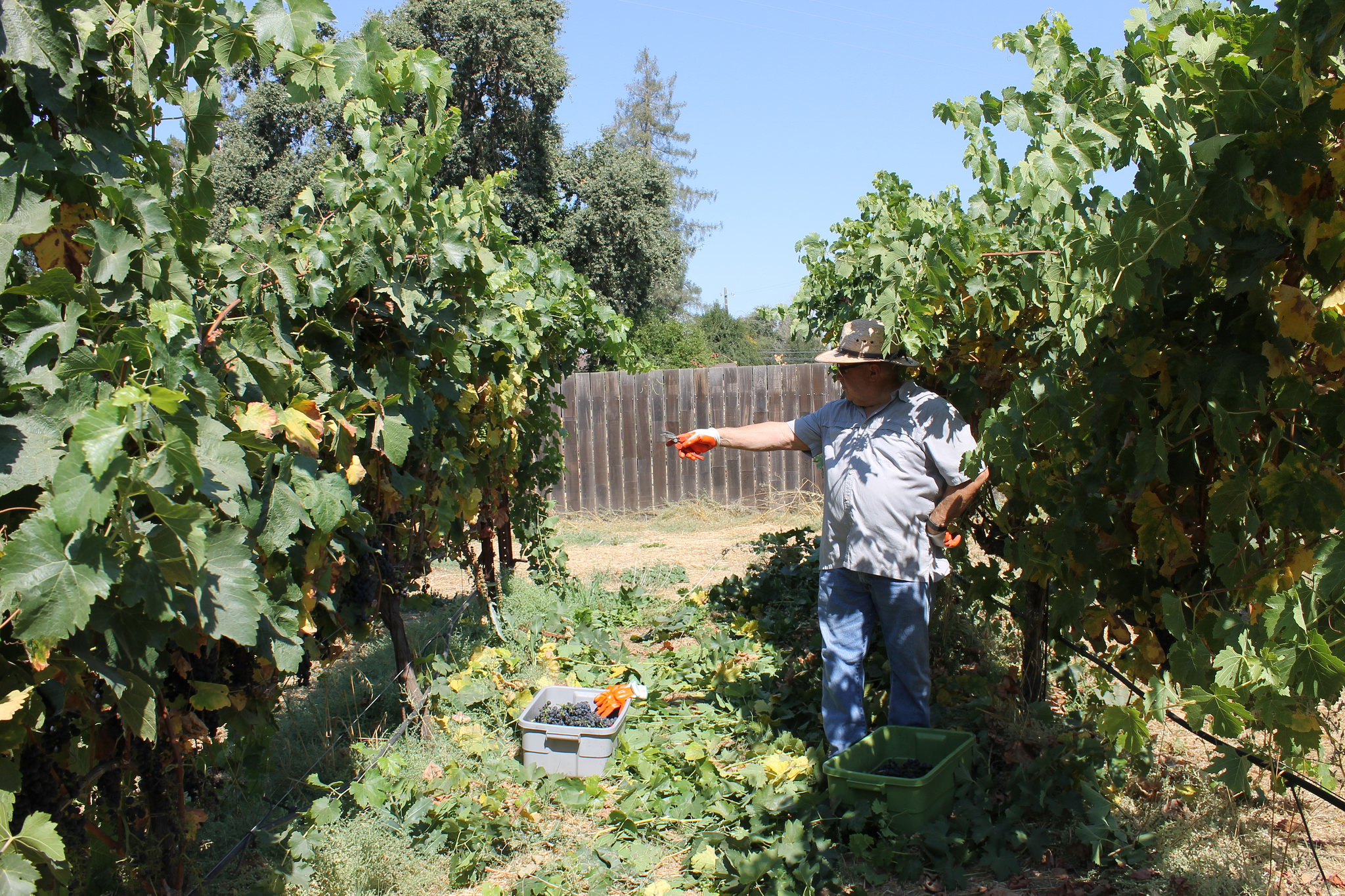
You can’t make a living on 500 cases.
Winemakers who are adaptable, not doctrinaire have the greatest chance for success. The trouble is, if your hit eclectic varietal is limited in acreage or is planted in a distant part of the state, how does a New Californian style winemaker follow up their big local winemaking hit if their resources are limited to 2 tons or roughly 100 cases? Or even 500 cases? You can’t make a living on 500 cases.
The next generation of start-up winemakers will have to have a portfolio of adaptable skills, both boutique and industrial. Winemakers have to be well versed in wine style, interventionist and non-interventionist, what sells to distributors, direct to bottle shops, sommelier driven restaurants and in the tasting room. The approach is practical, not dogmatic and not out of step with some of the winemakers in New California. Defining the terms natural and industrial seems to be the hottest topic in wine making these days, when only 5 years ago wine making was all about balance, as in pursuit of. How will natural be re-defined in 5 more years? How will the broad California appellation evolve?
Cabernet in Sonoma Vs. Barbera in Mendo
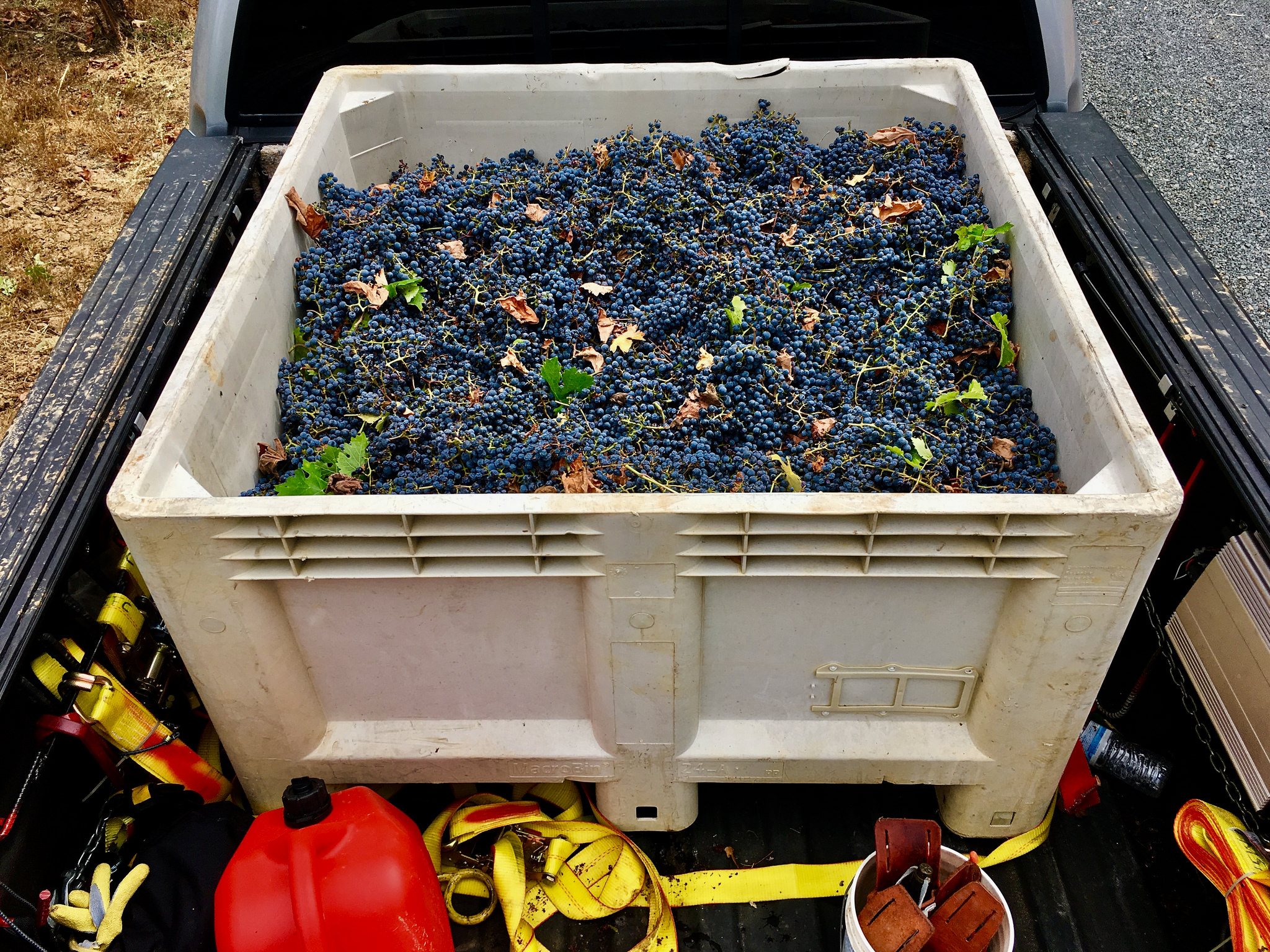
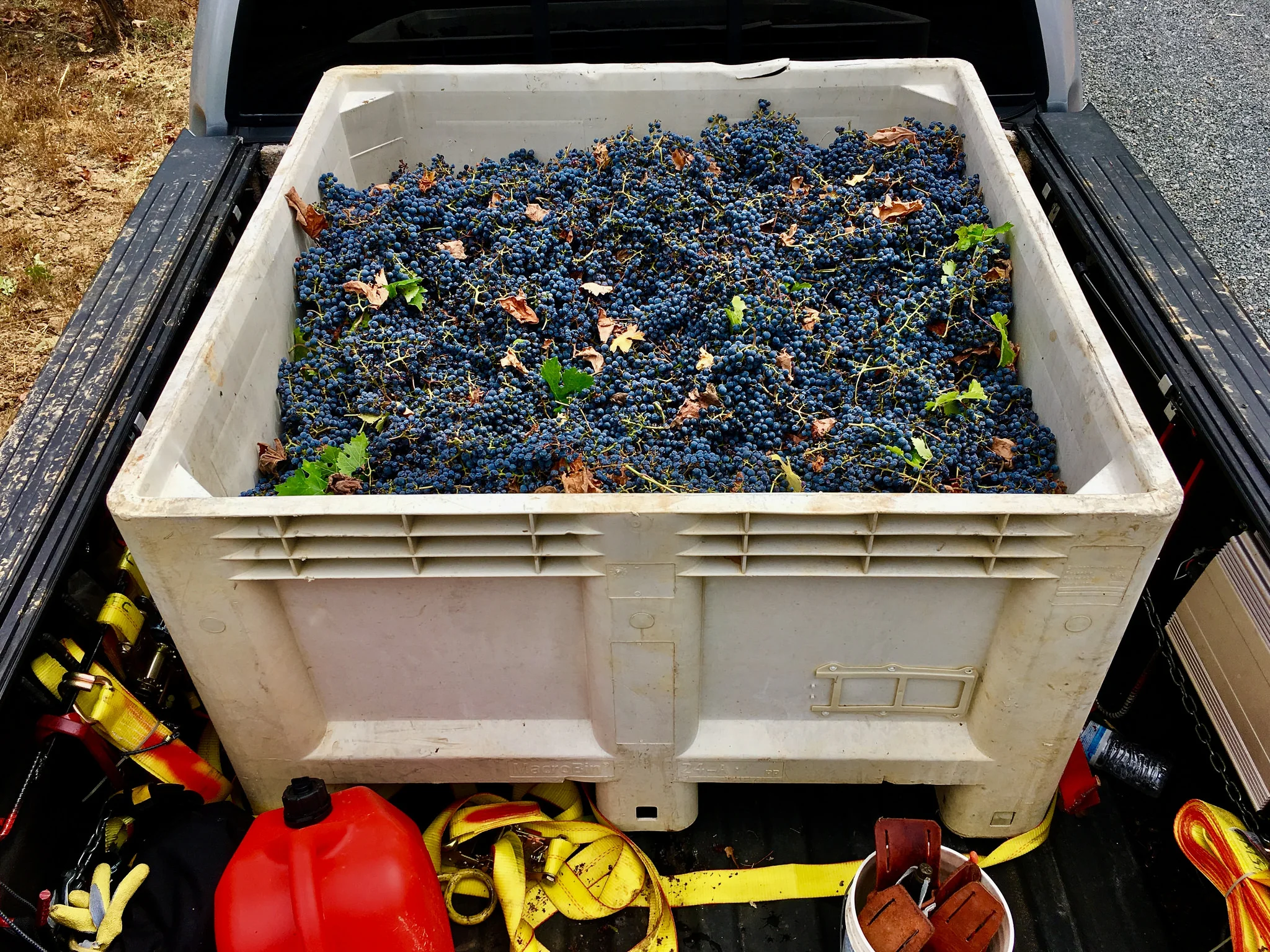
We as winemakers have to be both aggressive and flexible in simply finding fruit. I can find Cabernet in Sonoma County pretty easily if I can afford it. But I can’t find Sangiovese and Barbera, at least not at the price I’d like. I could go to the Foothills, but good luck if they deliver in 2 ton lots to Cloverdale. I could go to Lake or Mendocino County for a couple tons, but I’ll have to pick it up and prices aren’t $500/ton any more for small lots. Try closer to $1500/ton and many growers won’t sell 2 tons lots.
A wine sold at $25/bottle full retail is not a sustainable model for a stand-alone winery if the fruit alone sells for $2500/ton, not including crush fees. $2500 per ton and higher is not uncommon for many varietals in Sonoma County, my backyard. Winemaking can work as a side-hobby, but not as a self-sustaining business with a 500 case production, so don’t quit your day job.
Sure, there are pockets of small vineyards in Dry Creek and Alexander Valley looking to sell to “home winemakers”, but fruit quality and consistency can be painfully erratic. I know; I purchase from small farms every season. As winemaker, I have to be part time vineyard manager and viticulturist.
Mechanization
Lodi is already dealing with lower yields on old-vine Zinfandel and increases in labor and facility costs. Much of that planted acreage will sell to the highest bidder or simply be torn out and replaced with younger, more vigorous varietals and planted for mechanized harvesting. Recent articles show the increasing economic concerns of growers dealing with decreasing yields and increasing labor or skills costs. Mechanization is here and is growing.
There was (past tense) a wave of New Californian winemaker using forgotten varietals at cheap prices. Now, everyone is using them (again). Unfortunately, those varietals are more expensive as demand has increased, or simply, those vines have been ripped out in favor of more vigorous and popular varietals that demand higher prices.